As sustainability becomes a core requirement rather than a design trend, green building certifications like LEED and GRIHA are playing a decisive role in how buildings are planned, designed, and constructed. Architects and developers today are actively seeking materials that improve energy efficiency, daylight performance, thermal comfort, and environmental impact—all while remaining cost-effective and durable.
This is where polycarbonate sheets emerge as a smart, future-ready building material. From façades and skylights to roofing and partitions, polycarbonate significantly contributes toward achieving green building certifications when used correctly.
Understanding Green Building Certifications: LEED & GRIHA
Before diving into material performance, it’s important to understand what LEED and GRIHA evaluate.
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design)
Developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, LEED focuses on:
Energy efficiency
Indoor environmental quality
Sustainable materials
Innovation in design
Reduced carbon footprint
GRIHA (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment)
India’s national green building rating system, supported by TERI, evaluates:
Climate-responsive design
Energy and water optimization
Sustainable building materials
Waste reduction
Occupant comfort
Both certifications reward projects that integrate high-performance envelope materials—a category where polycarbonate sheets excel.
Why Polycarbonate Sheets Are Ideal for Green Buildings
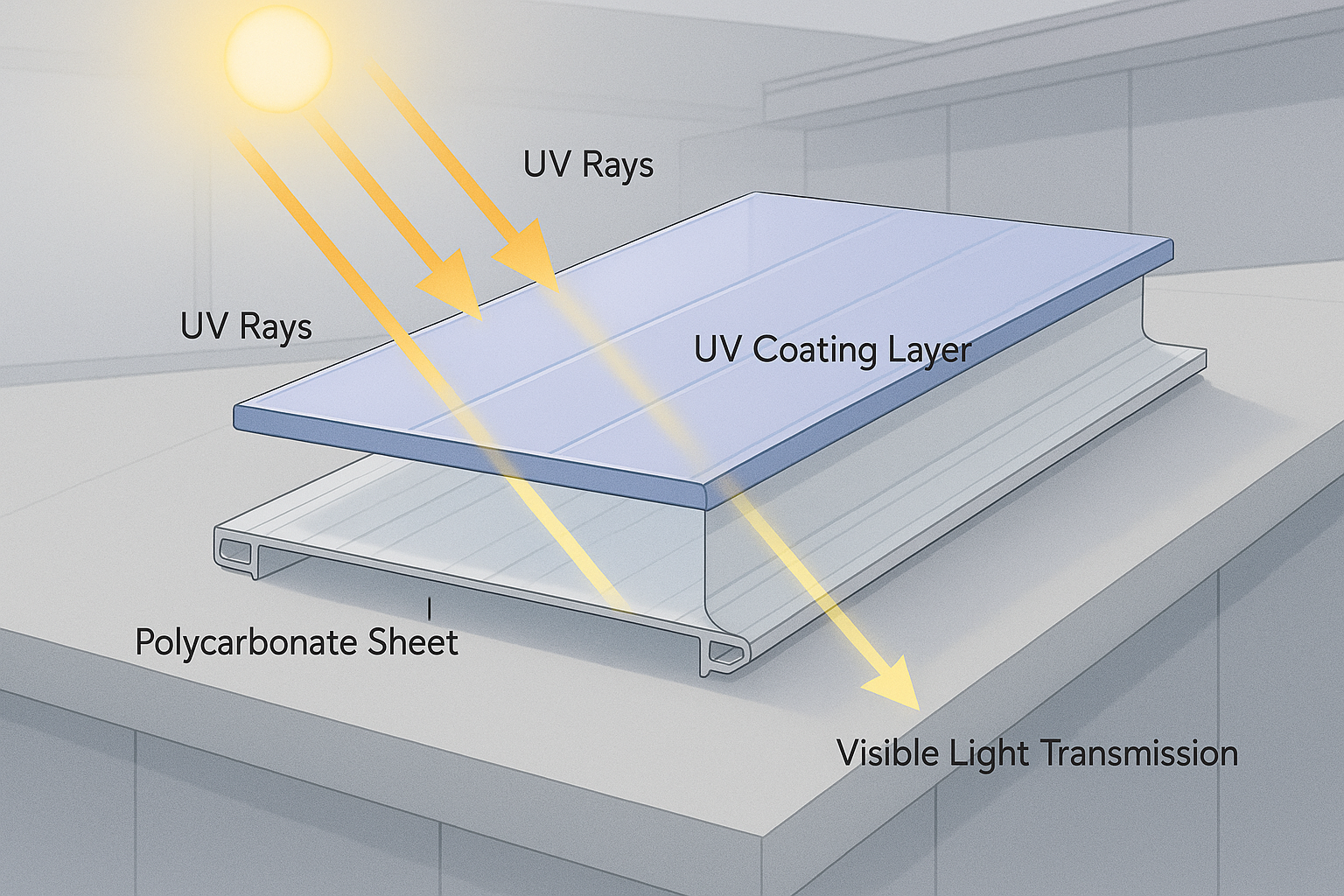
1. Daylighting & Reduced Artificial Lighting
One of the biggest contributors to LEED and GRIHA points is effective daylighting.
Polycarbonate sheets:
Transmit up to 80% natural daylight
Diffuse light evenly, reducing glare
Lower dependency on artificial lighting during daytime
This directly supports:
LEED Daylight Credit
GRIHA Visual Comfort & Energy Optimization criteria
Natural daylight not only saves energy but also improves occupant productivity and wellbeing.
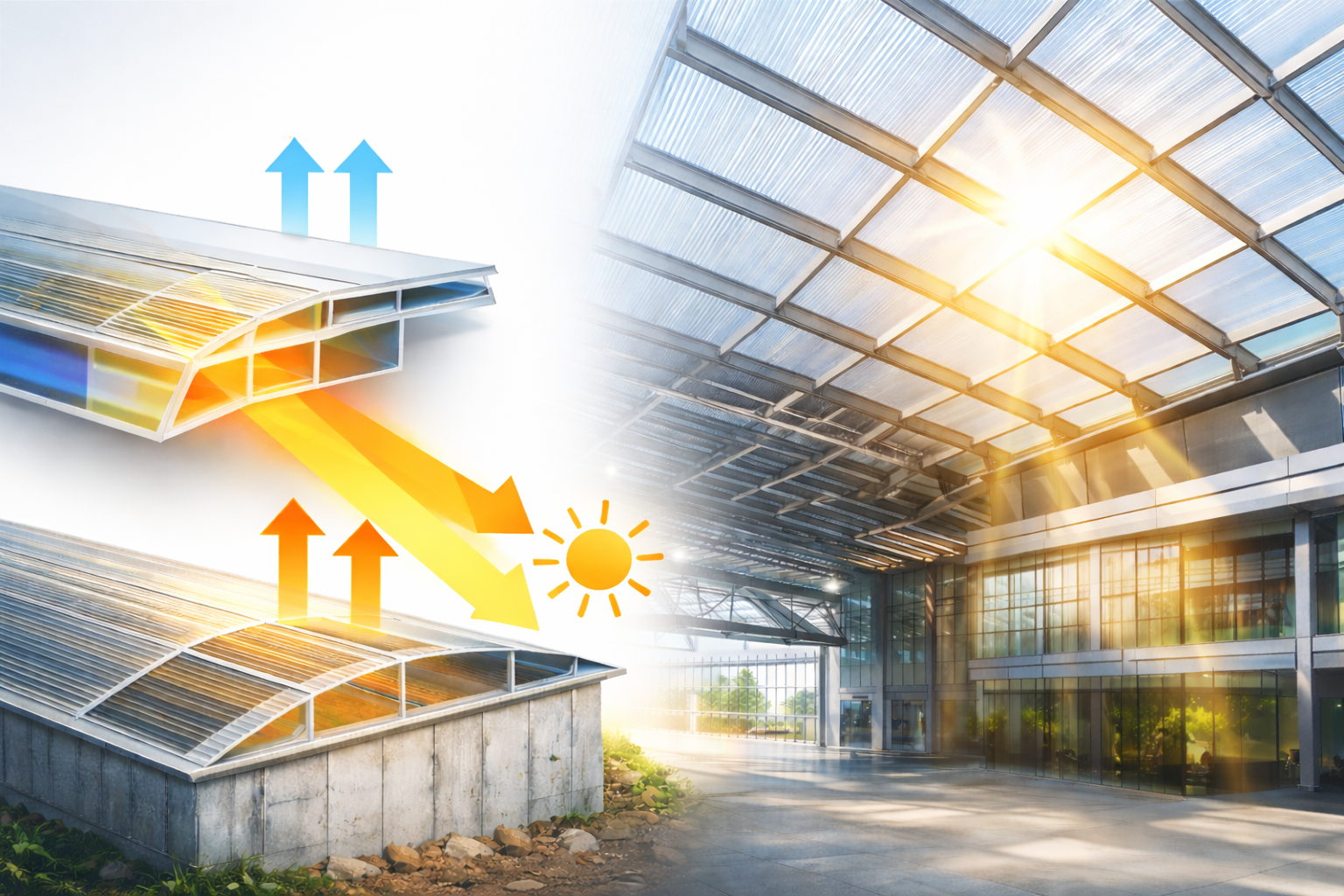
2. Superior Thermal Insulation & Energy Efficiency
Multiwall and multicell polycarbonate sheets trap air within their structure, creating excellent thermal insulation.
Benefits include:
Reduced heat gain in summer
Lower heat loss in winter
Decreased HVAC energy consumption
This improves:
Building envelope performance
Annual energy savings
Compliance with energy efficiency benchmarks under both LEED and GRIHA
3. Lightweight, Low-Carbon Construction Material
Compared to glass and conventional façade materials, polycarbonate sheets are:
Extremely lightweight
Easier to transport and install
Structurally efficient with less supporting steel
This results in:
Reduced embodied carbon
Lower construction energy
Better material efficiency scores under green building certifications
4. Recyclability & Sustainable Material Credits
Polycarbonate is a fully recyclable thermoplastic, aligning with circular economy principles.
Green certification advantages:
Supports LEED Materials & Resources credits
Meets GRIHA sustainable material selection guidelines
Reduces construction and demolition waste
Using recyclable polycarbonate sheets strengthens a project’s sustainability narrative and certification score.
5. Durability, Long Life & Reduced Maintenance
Durability is often overlooked—but it plays a key role in sustainability.
Polycarbonate sheets offer:
High impact resistance
UV protection against yellowing
Long service life with minimal maintenance
Longer material life means:
Fewer replacements
Lower lifecycle environmental impact
Improved building performance over decades
6. Design Flexibility Without Performance Compromise
Green buildings don’t need to sacrifice aesthetics.
Polycarbonate sheets can be used in:
Façades and curtain walls
Skylights and atriums
Roofing and canopies
Internal partitions and daylight panels
This design flexibility enables architects to achieve innovation points under LEED and integrated design credits under GRIHA.
Polycarbonate vs Glass in Green Building Design
| Parameter | Polycarbonate Sheets | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Daylight Diffusion | Excellent | High glare |
| Thermal Insulation | Very High (multiwall) | Low unless double/triple glazed |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Impact Resistance | Extremely high | Fragile |
| Sustainability | Recyclable, low carbon | Energy-intensive manufacturing |
This makes polycarbonate a performance-driven alternative to glass in certified green buildings.
Applications That Earn Green Building Points
Polycarbonate sheets are commonly used in:
Commercial buildings
Airports & metro stations
Educational institutions
Healthcare facilities
Industrial buildings
Public infrastructure projects
Each application contributes to daylighting, energy savings, material efficiency, and occupant comfort—key pillars of LEED and GRIHA.
Conclusion: A Smart Material for Certified Green Buildings
Achieving LEED or GRIHA green building certification requires thoughtful material selection—and polycarbonate sheets check all the right boxes. From energy efficiency and daylight optimization to recyclability and durability, polycarbonate supports sustainable construction at both design and performance levels.
For architects, developers, and consultants aiming to future-proof their projects, polycarbonate is not just an alternative—it’s a strategic advantage in green building design.